The Function of a Protein can be Identified by the Sequence and Structure of its Ligand-Defined Active Site
The Comparison of Protein Active Site Structures (CPASS) database and software is used as part of our FAST-NMR assay to assign the function of a hypothetical protein or a protein of unknown function. The CPASS database and software enable the comparison of experimentally identified ligand binding sites to infer biological function and aid in drug discovery. The CPASS database is comprised of unique ligand-defined active sites identified in the Protein Data Bank, and the CPASS program compares these ligand-defined active sites to determine sequence and structural similarity without maintaining sequence connectivity, along with ligand similarity, if desired. CPASS will compare any set of ligand-defined protein active sites irrespective of the identity of the bound ligand.
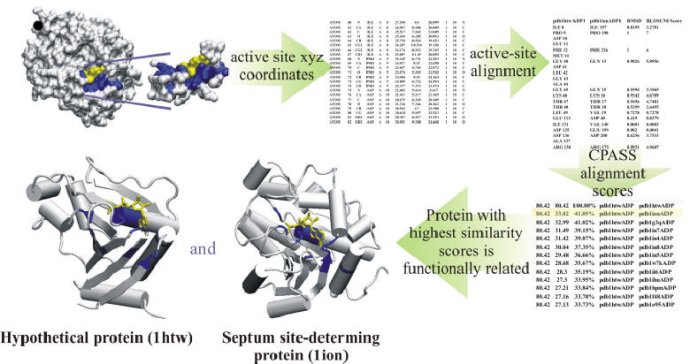
A ligand-defined active site is made up of every amino acid in the protein that contains at least one atom within 6 Å of the ligand. The CPASS database contains ~35,000 unique ligand-defined binding sites. The CPASS program determines the alignment of active site a with active site b from the CPASS database by maximizing an RMSD weighted BLOSUM62 scoring function (SAB), which includes the RMSD's between the Cα and Cβ residues, along with the surface accessibility of the residues and the RMSD between the ligands:
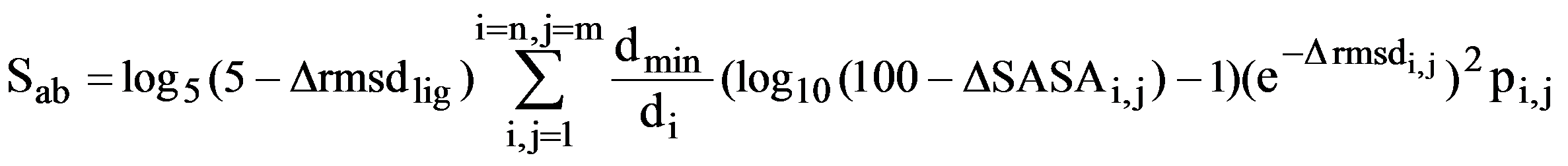
where Δrmsdlig is a corrected root-mean square difference between the ligands that define the two binding sites and ΔSASAi,j is the difference in the solvent accessible surface area (SASA) between residues i and j. The similarity score (S) is simply the ratio of the scoring function determined by comparing a protein target active site against a reference active site (Sab) from the CPASS database with the scoring function of a protein target active site compared against itself (Saa).
The similarity score (S) is simply the ratio of the scoring function determined by comparing a protein target active site against a reference active site (Sab) from the CPASS database with the scoring function of a protein target active site compared against itself (Saa),
S = Sab/Saa * 100.
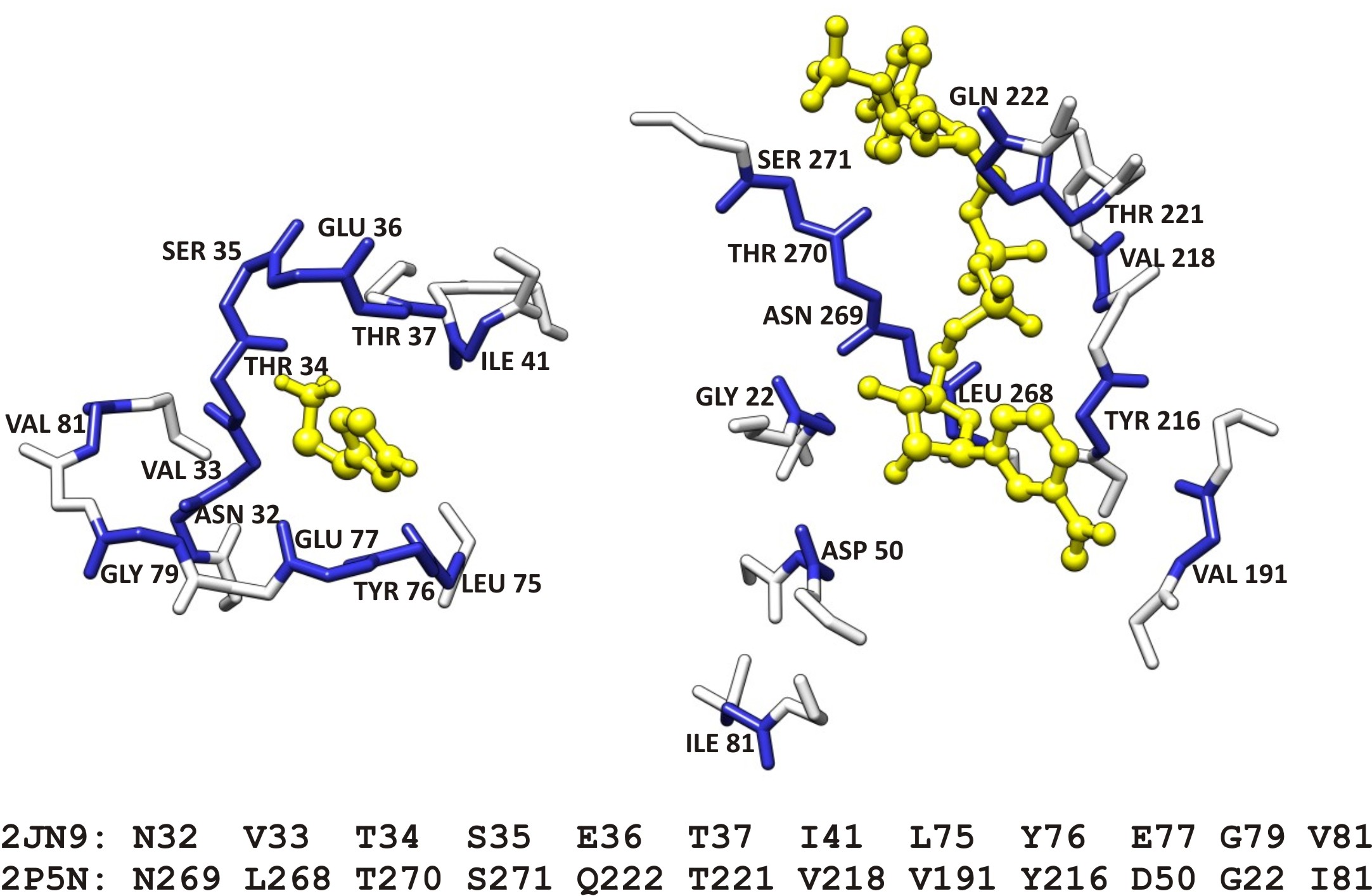
The following figure represents an example of an aligned active site of a hypothetical protein with a known formate dehydrogenase. The putative function for the hypothetical protein, derived from CPASS information as well as bioinformatics, is that of a stress-response dehyrogenase.
CPASS is free to use for academic users. However, you must register for access.
An email address from a valid academic institution is required for registration.
References
Publications related to CPASS
- J. Catazaro, A. Caprez, D. Swanson and R. Powers (2019) "Functional Evolution of Proteins." Proteins, 7(6):492-501 PMC6462239.
- J. Catazaro, A. Caprez, A. Guru, D. Swanson, and R. Powers (2014) "Functional Evolution of PLP-dependent Enzymes based on Active-Site Structural Similarities." Proteins, 82(10):2597-2608 PMC4177364 (cover).
- R. Powers, J. Copeland, J. Stark, A. Caprez, A. Guru, and D. Swanson (2011). "Searching the protein structure database for ligand-binding site similarities using CPASS v.2." BMC Research Notes, 4:17.
- R. Powers, J. Copeland and K. Mercier (2008) “The Application of FAST-NMR for the Identification of Novel Drug Discovery Targets.” Drug Discovery Today 13(3-4):172-179.
- R. Powers, J. Copeland, K. Germer, K. A. Mercier, V. Ramanathan and P. Revesz (2006) “Comparison of Protein Active-Site Structures for Functional Annotation of Proteins and Drug Design.” PROTEINS: Struct. Funct. Bioinformatics, 65(1):124-135.